X680v1.3 Software & Configuration
PiKVM
PiKVM is a Free and Open Source Software released under the GPLv3 license. The Operating System (OS) image provided here is solely for hardware testing. For commercial use, it is advised to directly contact the developers of PiKVM.
The development of this software would not be possible without the financial backing of the community. Contributions play a vital role in sustaining and advancing the project. Your support is greatly appreciated and will help in the continuous development and improvement of this software.
*Compatible with PiKVM V3 platform OS version only, not support V4.
*Does not support PiKVM Mass Storage Device as the integrated USB hub supports data sharing between 4 target hosts and can also be used for one of them, which will be available even in BIOS/UEFI when you need a live disk to revive the OS or even reinstall it.
Flash the image How to install Raspberry Pi Imager
Raspberry Pi Imager is free to install from the official Raspberry Pi website. It's available for MacOS, Windows, and Ubuntu systems.
- Visit the Raspberry Pi download page.
- Download the Raspberry Pi Imager installer for your Operating System.
- Run the installer and follow the prompts to complete the setup.
- Launch Raspberry Pi Imager.
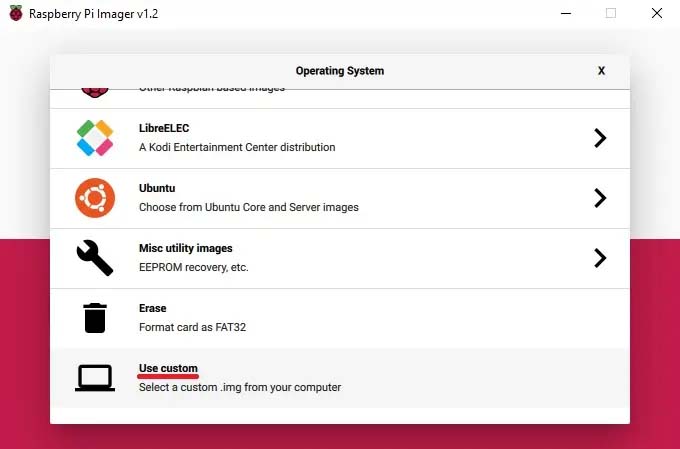
- Click "Choose OS".
- Select "Use custom" to write an unlisted image.
- Click "Choose SD card".
- Select from the list the SD card you want to write to.
- Click "Write" to begin the image writing process.
When the imager is finished, you can connect your microSD card to the Pi and boot it up.
Raspberry Pi Imager alternatives
If for whatever reason you don't want to or are unable to use Raspberry Pi Imager, you can opt to use an alternative application. Here are a couple we've relied on over the years:
- BalenaEtcher - The application runs on Windows, MacOS, and Ubuntu operating systems.
- Win32 Disk Imager - This imaging software is designed for Windows machines.
Programming the Compute Module
To program the Compute Module with EMMC, an external “host” PC is connected to the compute module USB Type-B port on the rear panel. After connecting the USB cable and running the “Rpiboot” utility, the Compute Module 4 will then appear as a USB device to the “host” PC, allowing it to be programmed.
 Host USB Connection for eMMC Programming
Host USB Connection for eMMC Programming
- Connect the power supply (5V 4A).
- Locate a USB port on your PC/laptop and connect using a USB 2.0 A to B cable.
- Important: Remove the USB cable after programming is complete.
Configuring the OS
- Access the PiKVM Web Interface via any browser with the URL: https://pikvm/ or https://[IP address of your PiKVM]/.
- Log in to PiKVM and click "Terminal".
- Get root access (enter the root password: Root).
- To enable write-mode, run the command: rw
- Run the following command to enable OLED: systemctl enable --now kvmd-oled kvmd-oled-reboot kvmd-oled-shutdown
- Setting up the RTC: The RTC chipset is DS1307, please change the line from Dtoverlay=i2c-rtc,pcf8563 to Dtoverlay=i2c-rtc,ds1307 in /boot/config.txt.
- Save and exit by hitting CTRL + X, answering Y, and hitting Enter when prompted.
- Rotate the OLED display by 180 degrees (Optional): Change the line in /usr/bin/kvmd-oled from {"height": 64, "rotate": 2} to {"height": 64, "rotate": 0}.
- Save and exit by hitting CTRL + X, answering Y, and hitting Enter when prompted.
- To disable write mode, run the command: ro
- Reboot the system.
CSI-2 bridge Connection test
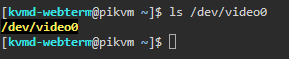
Make sure that the ‘/dev/video0’ device is available. Use this command to check: ls /dev/video0
If you see anything other than ‘file not found‘, then it’s available.
For further assistance or inquiries, please reach out to our support team at info@edgecase.shop or sales@edgecase.shop. We are here to help you with any questions you might have.